What are non-KYC exchanges?
Cryptocurrency trading platforms that do not verify users’ identities while onboarding them are called non-KYC exchanges.
Such platforms prioritize user anonymity and privacy, unlike KYC-compliant exchanges , which require users to provide personal information such as government-issued IDs, addresses and sometimes even financial details.
Non-KYC crypto exchanges can operate as custodial, non-custodial or hybrid forms. Each comes with its own risks amid a lack of regulatory oversight.
- Custodial non-KYC exchanges: These are centralized and hold users’ funds and private keys , giving them complete control over assets.
- Non-custodial non-KYC platforms: Such exchanges allow users to control their own private keys and assets, offering more security.
- Hybrid models: These blend both, offering custodial services for certain assets while allowing self-custody for others.
The anonymity and privacy non-KYC exchanges offer are attractive features for individuals who value discretion, those who reside in regions with restrictive financial regulations or users who prefer to minimize their digital footprint.
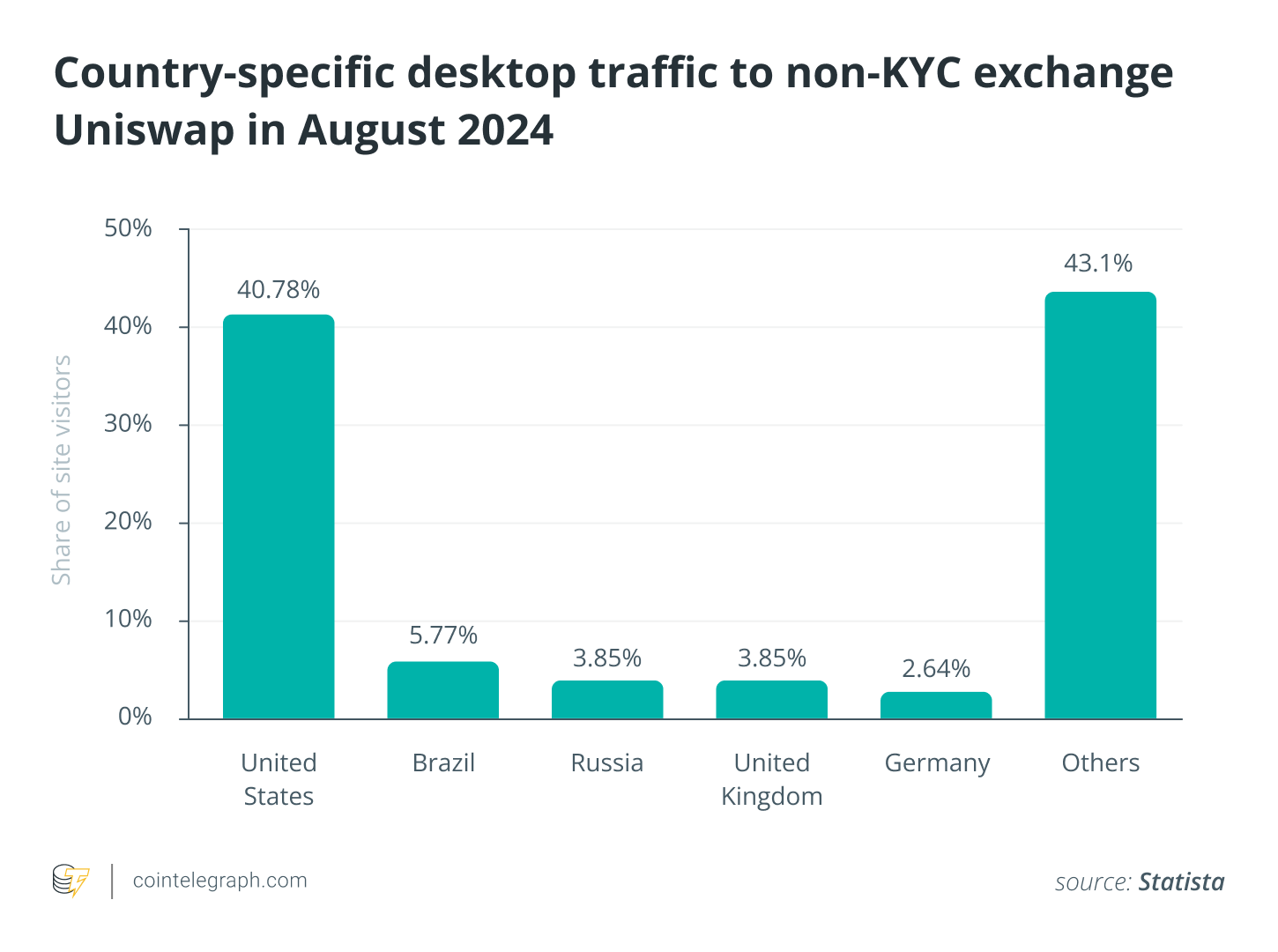
Still, the anonymity offered by non-KYC exchanges comes with risks you should be aware of before signing up on such platforms to buy, sell and trade digital assets.
What makes non-KYC exchanges riskier?
Risks associated with non-KYC exchanges can be broadly categorized into susceptibility to fraud and scams, regulatory oversight, security vulnerabilities and lack of transparency.
The relative freedom that the crypto market enjoyed over the past decade due to regulatory bodies either being slow to react or still formulating frameworks for digital assets is no longer the case.
Regulations like Anti-Money Laundering (AML) directives , Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) , and more stringent tax reporting obligations in jurisdictions like the EU and the US have transformed how exchanges operate.
Non-KYC exchanges are riskier because:
- Increased exposure to scams and fraud: Because they are anonymous, non-KYC exchanges are a haven for scammers . Due to a lack of legislation and control, these platforms are subject to frequent exit scams in which funds disappear as exchanges abruptly close. Fraudsters can manipulate markets and carry out schemes without identity verification.
- Stronger regulatory oversight: Regulatory frameworks like MiCA have tightened control over crypto exchanges, including offshore ones. Non-KYC platforms that avoid AML and KYC regulations are increasingly considered intermediaries for illicit activity. Authorities are closing down exchanges that don’t comply, fining individuals who use them and even detaining those who operate them.
- Security vulnerabilities: Non-KYC exchanges lack the mandatory cybersecurity measures of regulated platforms. Without frequent audits and stringent security measures, these exchanges become easy targets for hackers . Due to inadequate security, non-KYC platform users are more likely to lose their money, especially if these platforms come under increased scrutiny.
- Lack of transparency and legal recourse: Non-KYC exchanges frequently have opaque financial stability and operational policies. In the event that money is stolen or conflicts emerge, users have limited legal protection. Users of non-KYC platforms are vulnerable and may lack redress in the event of issues because there are neither external audits nor consumer protection regulations.
Did you know? OKX, once known for being a non-KYC platform, transitioned to a full KYC model after a regulatory crackdown, requiring all users to complete identity verification to comply with global regulations and ensure user security.
Understanding the legal implications of non-KYC platforms
Regulations vary by jurisdiction, meaning that the legal implications of using non-KYC platforms can be significant and multifaceted, and are heightened in regulatory environments where KYC and AML compliance is strictly enforced.
First, AML regulations, which are intended to stop illicit activities like money laundering and terrorism financing, may be violated by non-KYC platforms. Financial institutions, including cryptocurrency platforms, are required to implement KYC and AML procedures in many jurisdictions, especially those that follow the Financial Action Task Force’s (FATF) guidelines. Platform operators may be subject to fines, penalties or legal action for breaking these rules.
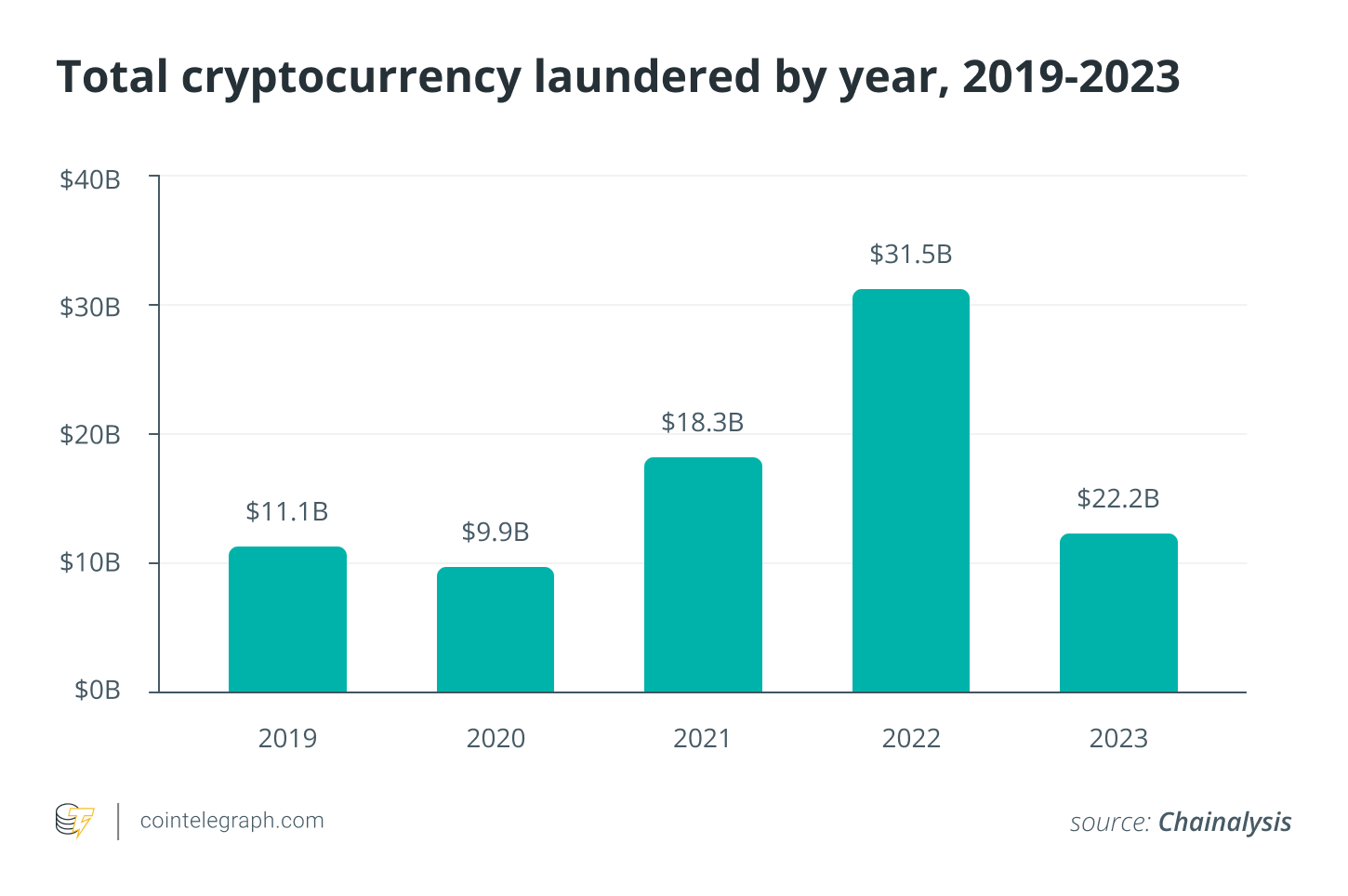
Additionally, by avoiding Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements, these platforms may limit their ability to operate in certain countries. For example, regulators in the United States, the European Union, and several other regions have strict rules on customer identification.
Platforms that fail to meet these requirements may be restricted from offering services to users in those jurisdictions. Authorities in some regions have taken steps to blacklist or block access to non-compliant platforms.
Moreover, users of non-KYC platforms can be subject to legal consequences. Using a platform that does not follow KYC criteria may be interpreted as enabling illegal financial activities, depending on local laws. Even if a user’s actions are unintentionally linked to illegal financial activity, they could still face consequences.
Risks of anonymous crypto trading
Anonymous crypto trading exposes users to legal, financial and security risks due to lack of regulatory compliance and accountability.
Here are the risks you should be aware of:
- Platform shutdowns: Non-KYC exchanges are more vulnerable to being shut down or blacklisted by regulatory authorities, potentially leading to loss of access to funds.
- Association with illicit activities: Anonymous trading can inadvertently involve users in illegal activities such as money laundering, fraud or terrorism financing , increasing the risk of legal repercussions.
- Asset seizure: Authorities may seize assets or freeze accounts associated with non-compliant exchanges during investigations into unlawful transactions.
- Legal exposure: Engaging in transactions on anonymous platforms may violate national laws, especially in countries that require KYC and AML compliance for financial services.
- Limited recourse for disputes: Anonymous platforms often offer little to no protection in case of transaction disputes, hacking incidents or loss of funds.
- Increased fraud risk: Without KYC, there is a higher chance of encountering fraudulent actors or scams, as the lack of identity verification reduces accountability.
- Difficulty in tax reporting: Anonymous transactions can complicate compliance with tax reporting obligations, potentially leading to penalties for non-disclosure.
Did you know? BitMEX, a major crypto derivatives platform, was fined $100 million in 2021 for failing to implement proper KYC and AML procedures , as regulators found it had facilitated illegal transactions, including money laundering.